Copyright or author’s right is a form of knowledge protection. It is the legal term used to detail creators rights about literary and artistic works. Works covered by copyright goes from books, music, paintings, sculpture, and films, to computer programs, databases, advertisements, maps, and technical drawings.
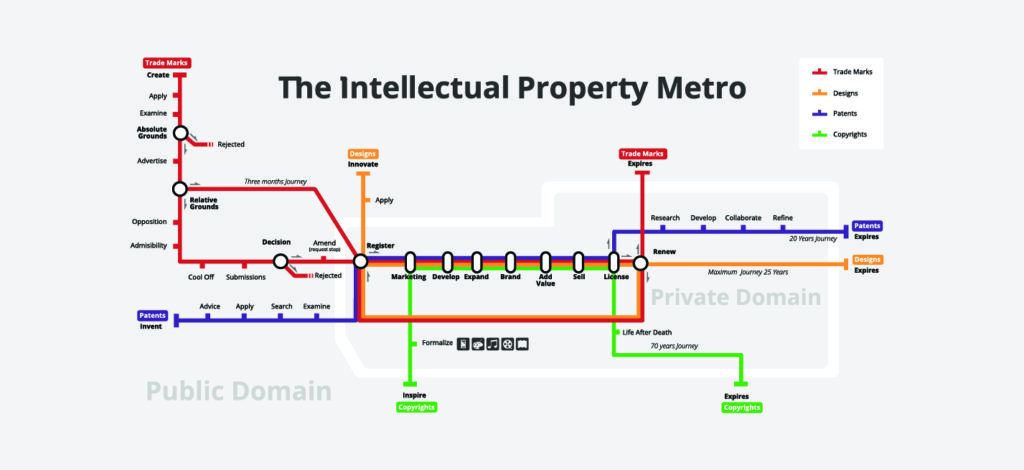
Copyright features:
- Protected object: literary works such as novels, books, poems, plays, newspaper articles, reference works; computer programs and databases; films, musical compositions and choreography; artistic works such as paintings, photographs, drawings and sculpture; architecture; advertisements, maps, and technical drawings.
- Type of protection: economic and moral rights. Economic rights allow the owner to derive financial reward from the use of the work and moral protect the non-economic interests of the author.
- Duration: The author’s entire life plus 70 years after his death (Spain), but this can vary according to national law. In countries members of the Berne Convention, the time limit should be equal to or longer than 50 years after the creator’s death. Longer periods of protection may, however, be provided at a national level.
- Type: Registration is not required. Copyright protection is obtained automatically without the need for registration or other formalities under de Berne Convention.
- Competent Body: Most countries have a system for the registration and optional deposit of works, although their registration is voluntary.
Copyright protection extends only to expressions and not to ideas, procedures, methods of operation or mathematical concepts as such. Copyright may or may not be available for several objects such as titles, slogans, or logos, depending on whether they contain sufficient authorship.
More information: #MoocVT Module 2: Technology information management.