The setting-up of a technology-based firm, also known as a spin-out or startup company, is one of the main technology transfer strategies to bring research to market. New technology developments are strategic sources of information, and this guide aims to give a brief overview of the key aspects that support the spin-out creation and development process:
Spinouts and startups companies and business
- Academic spinouts:
Spinouts companies are created within another organisation, which can be a firm, an academic institution or a research institute. They are a spread-out mechanism to transfer applied scientific knowledge to society and are submitted to the changing legal framework. - Business startups:
Startups are also coming from innovative business ideas, but they are not created inside of an institution. They are knowledge-intensive and due to exploiting new technologies, products, processes or services in the market. The goal is to exploit a market niche, although also limited in time, but in a more agile, innovative and independent way.
Legal framework
Academic Spin-outs are subject to the national legal framework affecting its creation and development process. Mostly reflects on the research staff participation in the company’s share capital and governing bodies. Their time dedication and technology transfer mechanisms are involved. While this policy deals strictly with internal stakeholders, all parties involved should receive a reward that reflects the risks undertaken. Some examples are:
Conditions and requirements for Spin-out creation
The identification and protection of an intellectual property asset is the basis for a company worth forming. The main issues that should be controlled are briefly described here:
- To have control of the technology with commercial potential. It should be mature enough (with high TRL) and a proven business opportunity in the market.
- To commit with leadership within the entrepreneurial project with a devoted and multidisciplinary team, both should combine technological development with business management. This is a strategic issue for investors.
- To develop a novel, competitive and feasible business model based on the product or service.
- To efficiently protect scientific knowledge as a source of competitive advantages and intangible assets, as suggested by the Intellectual Property Guide for Startups recently developed by WIPO.
- To develop a novel, solid and reasonable business strategy to access the market.
- To develop a parallel networking strategy for the integration of the future company in the innovation ecosystem.
These strategic factors guide the technology-based company development stages. It requires an intense effort of strategic intelligence to market, key players and business understanding.
Besides, most universities and research institutions have support units to guide entrepreneurship initiatives, that is the case of UA: Emprende, University of Alicante entrepreneurship program.
Entrepreneur Tools
The conventional business plan for the conception of technology companies is in constant development and the globalization of scientific knowledge is an increasingly complex, changing and volatile environment. This implies agile and flexible tools application to allow business proposals with guarantees of survival and sustainability. The most useful entrepreneur tools are:
Technology intelligence represents a reliable information strategic tool for entrepreneurs. In #MoocVT you will find insights such as the Technology Monitoring Canvas Model as examples.
Funding Tools
Funding is a decisive issue in the life cycle of a technology-based company. Hence, it is necessary to design a financing strategy from the first stage, as well as participate in business rounds to capital raise. Funding sources are structured according to the different business growth stages. In consequence, each business development phase involves specific problems with different financial requirements.
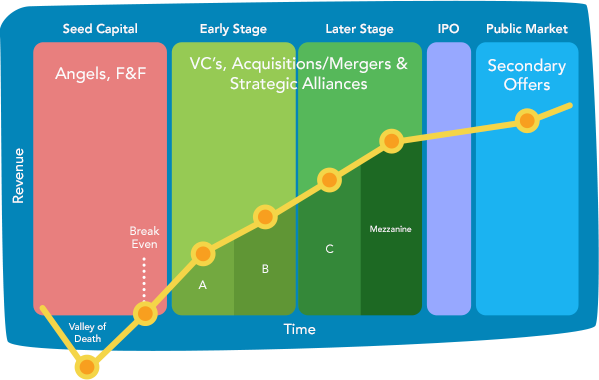
The most common funding instruments for early stages are focused on providing shape to the business idea, some examples can be:
- Promotors and founders’ own funds, both contribution with knowledge, time and dedication to the business project when still there are no benefits.
- Family, friends and fools: those people close to entrepreneurs willing to contribute with small amounts of money to develop the business idea.
- Business Angels: generally experienced individual investors who inject capital into the startup business.
- Accelerators: specialized organizations that promote competitions and prizes to contribute both with capital and advice in the early stages of an entrepreneurial project.
The most common funding instruments for start-ups and spin-outs in the seed capital stage are oriented towards the development of a launching product and to its sustainability in the market. The main goal at this point is to overcome the well-known “valley of death” and expand financing options towards :
- Venture capital: through professional companies, funds and investors.
- Crowdfunding: with modalities such as equity crowdfunding where investors contribute with capital and receive back a company share.
- Funding rounds for capital raise.
- Grants, loans and funding programmes.
- Mutual guarantee companies to access loans with better conditions.
- Participative loans aimed at long-term financing investments, which can later be converted into their own capital.
- Self-financing: relative to those funds generated over the course of the start-up’s business activity.
Technology intelligence is a required tool for locating funding and opportunities in technology-based companies development. Therefore, in MoocVT you will find more information regarding this issue.